Metal Roof Coverings
These are generally used for steep-slope roofs rather than for low-slope roofs. See Art. 12.5.3. However, some standing-seam structural panel systems can be used successfully in low-slope situations. These systems are considered hydrostatic, that is, they have the ability to resist water intrusion under some pressure. These panel systems generally incorporate a sealant in the seam, or an anti-capillary hem to provide the necessary protection from moisture infiltration through the seams.
Modified Bitumen Membranes
These are typically composed of prefabricated sheets of polymer-modified asphalt with polyester or glass-fiber reinforcement or a combination of these. The polymers most used for asphalt modification are atactic polypropylene (APP) or styrenebutadiene- styrene (SBS). These prefabricated sheets are commonly installed over a base sheet (Art. 12.4.1), which may or may not also be composed of modified bitumen. Sometimes the assembly also includes a ply sheet (Art. 12.4.1).
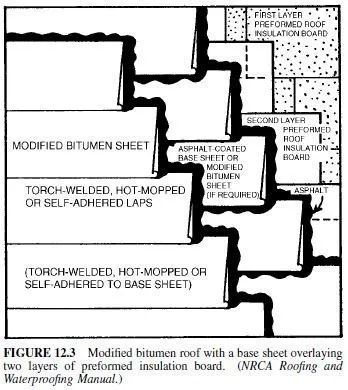
In the past, modified bitumen membranes were occasionally applied in a single layer. However, two or more layers are now the predominant system (Fig. 12.3).
SBS sheets are generally set in a continuous layer of hot asphalt, but some sheets may be torch-applied or set in cold adhesive. Self-adhering styrene-ethylenepropylene- styrene (SEPS) sheets are also available. SBS and SEPS sheets need protection from ultraviolet light (UV). Protection is typically provided by factoryapplied mineral granules. They may also be surfaced with coatings (Art. 12.4.1).
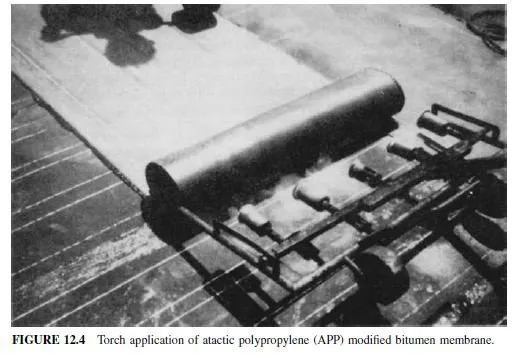
APP sheets are generally torch-applied (Fig. 12.4). When APP sheets were introduced in the United States in the late 1970s, they were generally used without surfacing, since UV protection was reportedly provided by the APP modifier. While some such APP membranes weathered very well, others did not. Hence, coatings (cutbacks, emulsions, or latex) or granules are now often used.
The ASTM material standards for polymer-modified bitumen sheet products are as follows:
ASTM D6162, Standard Specification for Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS)
Modified Bituminous Sheet Materials Using a Combination for Polyester and Glass Fiber Reinforcements
ASTM D6163, Standard Specification for Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS)
Modified Bituminous Sheet Materials Using a Glass Fiber Reinforcements
ASTM D6164, Standard Specification for Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS)
Modified Bituminous Sheet Materials Using Polyester Reinforcements
ASTM D6222, Standard Specification for Atactic Polypropylene (APP) Modified Bituminous Sheet Materials Using Polyester Reinforcements
ASTM D6223, Standard Specification for Atactic Polypropylene (APP) Modified Bituminous Sheet Materials Using a Combination of Polyester and Glass Fiber Reinforcements
ASTM D6298, Standard Specification for Fiberglass Reinforced Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS) Modified Bituminous Sheets with a Factory Applied Metal Surface
For each of these standards, except ASTM D 6298, type classifications (e.g., Type I, Type II) differentiate products (covered by the same standard) by the products dimensions, masses and physical properties. In addition, grade classifications differentiate products by the products surfacing type: Grade G designates granule surfacing and Grade S designates smooth surfacing.
Instead of incorporating prefabricated modified bitumen sheets, membranes can also be constructed with modified mopping asphalt and felts (of the type used for BUR construction). For modification of asphalt for application by mopping or bymechanical spreaders, styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS) polymers are utilized.