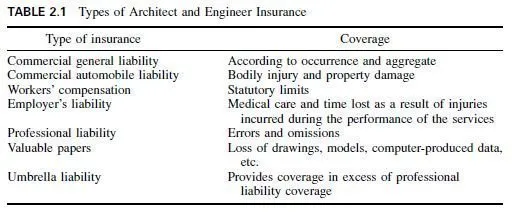
Aluminum connections also may be bolted or riveted. Bolted connections are bearing type. Slip-critical connections, which depend on the frictional resistance of joined parts created by bolt tension, are not usually employed because of the relatively low friction and the potential relaxation of the bolt tension over time.
Bolts may be aluminum or steel. Bolts made of aluminum alloy 7075-T73 have a minimum expected shear strength of 40 ksi. Cost per bolt, however, is higher than that of 2024-T4 or 6061-T6, with tensile strengths of 37 and 27 ksi, respectively.
Steel bolts may be used if the bolt material is selected to prevent galvanic corrosion or the steel is insulated from the aluminum. One option is use of stainless steel. Another alternative is to galvanize, aluminize, or cadmium plate the steel bolts.
Rivets typically are made of aluminum alloys. They are usually driven cold by squeeze-type riveters. Alloy 6053-T61, with a shear strength of 20 ksi, is preferred for joining relatively soft alloys, such as 6063-T5, Alloy 6061-T6, with a shear strength of 26 ksi, is usually used for joining 6061-T6 and other relatively hard alloys.