The primary purpose of a floor covering in an industrial building is to protect the structural floor from foot and truck traffic and from corrosive affluents. The flooring also must provide a durable surface that will not be detrimental to plant operations.
A good-quality concrete floor is adequate if factory conditions are dry and the surface has to withstand only foot and truck traffic. A cast-iron grid filled with concrete on 1â„4-in-thick steel plates may be used in areas where heavy equipment or materials are dragged continually. End-grain wood blocks may be used in areas of heavy trucking of heavy castings, to protect both the structure and castings from impact damage. Asphalt mastic floors also are used in areas with heavy truck traffic.
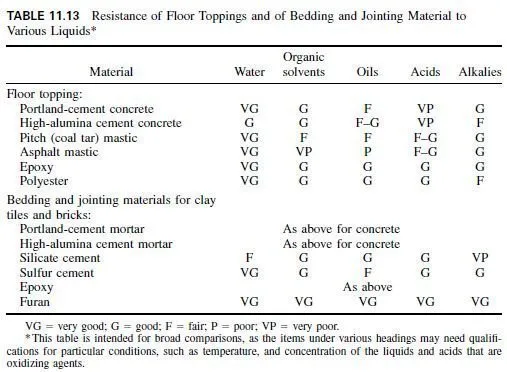
If the factory process is wet and corrosive, the designer may have to choose between a less-resistant flooring that has to be replaced periodically and a flooring with low maintenance costs but high initial cost. Table 11.13 rates the relative resistance to liquids of some floor toppings and bedding and jointing materials for clay tiles and bricks. In addition to selecting the most suitable materials, the designer should provide adequate slope and drainage, a liquid-tight layer below the finished floor as a second line of defense, and a nonslip surface. Selection and laying of chemical-resistant materials are a specialized operation on which specialists should be consulted.