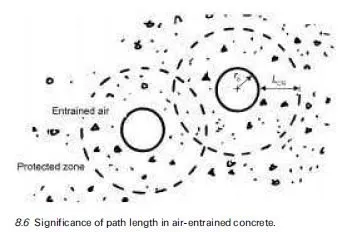
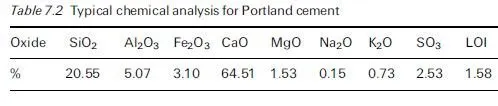
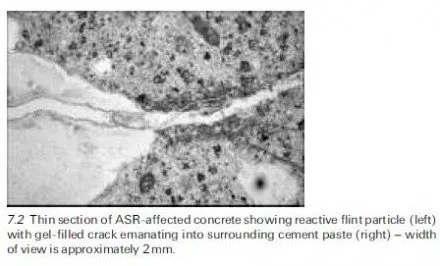
Areas of corrosion in prestressing tendons pose a considerable risk for prestressed concrete members. Flaws in the ducts also expose the steel tendons to hydrogen-induced stress corrosion.
The half-cell potential mapping method can be used for the detection of corrosion of tendons in pre-tensioned concrete.6 It is not, however, appropriate for the detection of corrosion in tendons in post-tensioned concrete, since it cannot monitor what is happening to the tendons within the metal or plastic ducts within which they are housed. In this method, the differences in potential between the tendon and a suitable reference electrode placed at various points on the concrete surface are measured (Fig. 6.16). The concrete surface is moistened to provide sufficient electrical conductivity. In general, corrosion is greatest at positions of high negative potential with large potential gradients around them. However, reliable conclusions about possible corrosion cannot be drawn from individual potential values. The cumulative percentage curve, which shows the percentages of readings as a function of potential, provides a useful analysis method in practice.68 An inflection point in this curve indicates the existence of active corrosion.
Additional information on the electrochemical condition of tendons may be obtained by means of linear polarisation or by pulse techniques, as described elsewhere.70,71 An example of the latter is the galvanostatic pulse technique, in which a small constant electrical current is applied to the tendon via a counter electrode on the concrete surface and the steel potential is monitored as a function of time (Fig. 6.17). The analysis of the transient response of the measured potential from the starting time to the steady state with the potential Vmax leads to the following simplified relation between the resistance (R ) of the concrete, the charge transfer resistance of the steel/concrete interface (R) and the capacitance (C) of the double layer:
![]()
The parameters R , R and C can be determined from equation 6.3. Small values of R indicate the existence of active corrosion. This method has been claimed to work substantially better than the usual measurement of the rest potential, especially in the case of wet concrete.72 Electrochemical monitoring methods of the kind described above are well established. However, the measurement and interpretation of the results must be carried out by trained and experienced staff.